
Peering into the success stories of companies that have turbocharged their Asset Efficiency can be both enlightening and inspiring. Take, for example, a retail giant that fine-tunes its inventory turnover, leading to a significant lift in their ratio. Or a manufacturing company that invests in advanced robotics, boosting production without a proportional increase in assets.
Asset Management Ratios: Definition, Formula, Example, More
The operating asset turnover ratio, an efficiency ratio, is a variation of the total asset turnover ratio and identifies how well a company is using its operating assets to generate revenue. Your asset turnover ratio is an equation to help you figure out how you’re using your assets to generate sales. In much simpler terms, by finding your asset turnover, you can figure out how many dollars of sales you’re generating for every dollar in the value of assets you have.

What is the total asset turnover ratio? The meaning of the total asset turnover formula
This means that both companies have the same efficiency in using their assets, even though Company A has higher sales and assets than Company B. The fixed asset ratio formula focuses on how efficiently a company utilizes its fixed assets, such as real estate, plant, and equipment, to generate sales turnover ratio revenue. A higher fixed asset turnover ratio indicates effective utilization of these long-term assets, which can lead to improved profitability.
- The ratio excludes such line items in its calculation and, thus, provides information regarding how well revenue-generating assets are being utilized.
- Since companies have various types and classes of assets, there are also different ratios for different assets.
- The fixed asset turnover ratio formula divides a company’s net sales by the value of its average fixed assets.
- Assuming the company had no returns for the year, its net sales for the year were $10 billion.
- A value peaking above 1 whispers tales of effectiveness, showcasing that a company has been adept at using its assets to concoct a sum of sales exceeding the total value of its assets.
Low vs. High Asset Turnover Ratios
It’s being seen that in the retail industry, this ratio is usually higher, i.e., more than 2. AT&T and Verizon have asset turnover ratios of less than one, which is typical for firms in the telecommunications-utilities sector. These companies have large asset bases, so it is expected that they will slowly turn over their assets through sales. Average total assets are found by taking the average of the beginning and ending assets of the period being analyzed. The standard asset turnover ratio considers all asset classes including current assets, long-term assets, and other assets. There is no exact ratio contribution margin or range to determine whether or not a company is efficient at generating revenue on such assets.
Asset Turnover Ratio: Formula, Examples, How to Improve It
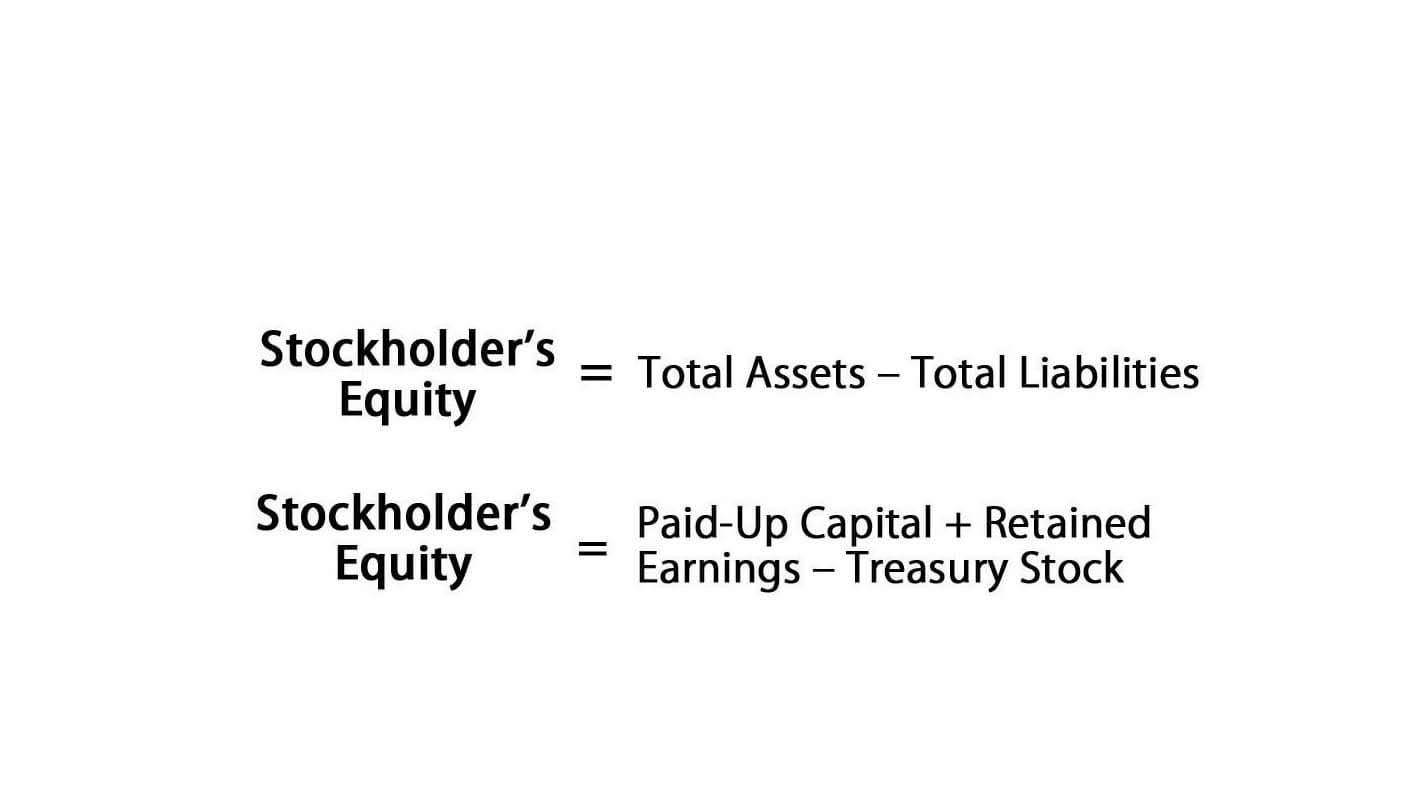
It is calculated by dividing net sales by the average balance of fixed assets of a period. The asset turnover ratio, also known as the total asset turnover ratio, measures the efficiency with which a company uses its assets to produce sales. The asset turnover ratio formula is equal to net sales divided by the total or average assets of a company. A company with a high asset turnover ratio operates more efficiently as compared to competitors with a lower ratio. The Net Asset Turnover Ratio measures how effectively a company generates sales from its net assets. Net assets refer to total assets minus total liabilities, representing the shareholders’ equity or the portion of assets owned by shareholders.

For Year 1, we’ll divide Year 1 sales ($300m) by the average between the Year 0 and Year 1 PP&E balances ($85m and $90m), which comes out to a ratio of 3.4x. For the final step in listing out our assumptions, the company has a PP&E balance of $85m in Year 0, which is expected to increase by $5m each period and reach $110m by the end of the forecast period. Suppose a company generated $250 million in net sales, which is anticipated to increase by $50m each year. Additionally, you can track how your investments into ordering new assets have performed year-over-year to see if the decisions paid off or require adjustments going forward. On the Bakery Accounting flip side, a turnover ratio far exceeding the industry norm could be an indication that the company should be spending more and might be falling behind in terms of development. Just-in-time (JIT) inventory management, for instance, is a system whereby a firm receives inputs as close as possible to when they are needed.
What Is Turnover Ratios Formula?
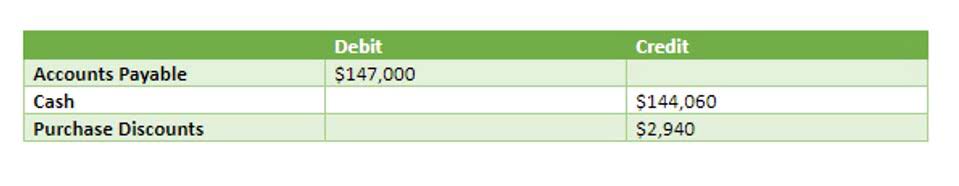
First of all, these ratios help determine the efficiency and effectiveness of a company. The Payables Turnover shows how quickly a company makes payments to its suppliers for credit purchases. Tighter control of inventory, including returns and damaged goods, will help you bring up your net sales number (and lower your cost of goods sold) and ultimately increase your assets turnover ratio. Understanding the differences and relationships between these ratios helps investors and managers asset turnover ratio make well-informed financial decisions.